JSONata bindings in Truto Unified APIs
Bindings are the building blocks you use in Truto Unified APIs to access and work with different parts of an API request and response. They're especially useful when writing JSONata expressions to transform data. When a JSONata expression runs, it uses these bindings to get the input data it needs. For example, query gives you access to all query parameters in a request. In this section, we will go through the JSONata Bindings available in Truto Unified APIs by each Mapping Type.
You can refer to Truto JSONata to know more about the JSONata methods supported.
Query Mapping
Available Bindings
query- Description: Contains the
queryparameters sent as part of the Unified API call
- Description: Contains the
body- Description: The request body associated with the Unified API call.
context- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
- Account Settings from
integratedAccount.context: These are persistent configurations specific to the connected account. - Information from
baseContext: This is used for passing certain info in Sync Jobs, such as the number of records for pagination (e.g., total_records_size).
- Account Settings from
You can access these properties directly in your integration logic. For example, to access the
authToken, usecontext.authToken.- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
before- Description: Contains the result of the
before stepscall.
- Description: Contains the result of the
id- Description: Can be used for cases when
idis present in Query Params, for example in/crm/accounts/:id
- Description: Can be used for cases when
Example
Scenario: User inputs contact.id which is mapped to person_id that the underying Salesforce API accepts. Here, contact is the Unified API resource that maps to Persons in Salesforce. To filter Accounts with a particular contact, we use the following query mapping
Query Mapping Configuration:
{
"person_id": query.contact.id
}Explanation:
query.contact.idaccesses thecontact.idparameter from the user's request.person_idis the internal parameter used by Salesforce.
Example Unified Request:
GET /unified/crm/accounts?contact[id]=12345Mapped Query Parameters:
{
"person_id": "12345"
}Body Mappings
Available Bindings
body- Description: The request body associated with the Unified API call.
query- Description: Mapped query parameters.
rawQuery- Description: The query parameters from the user's request before
querymapping.
- Description: The query parameters from the user's request before
context- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
- Account Settings from
integratedAccount.context: These are persistent configurations specific to the connected account. - Information from
baseContext: This is used for passing certain info in Sync Jobs, such as the number of records for pagination (e.g., total_records_size).
- Account Settings from
You can access these properties directly in your integration logic. For example, to access the
authToken, usecontext.authToken.- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
before- Description: Contains the result of the
before stepscall.
- Description: Contains the result of the
id- Description: Can be used for cases when
idis present in Query Params, for example in/crm/accounts/:id
- Description: Can be used for cases when
Example
Body Mapping Configuration:
{
"fullName": body.name
}Explanation:
body.nameaccesses thenamefield from the request body.fullNameis the field used by the underlying API.
Header Bindings
Available Bindings
headers- Description: The HTTP headers from the Unified API call.
query- Description: Mapped query parameters.
rawQuery- Description: The query parameters from the user's request before
querymapping.
- Description: The query parameters from the user's request before
body- Description: The request body associated with the Unified API call.
contextDescription: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
- Account Settings from
integratedAccount.context: These are persistent configurations specific to the connected account. - Information from
baseContext: This is used for passing certain info in Sync Jobs, such as the number of records for pagination (e.g., total_records_size). - Dynamic Runtime Values:
id: The unified model id that uniquely identifies the record.before: The before steps that run immediately before the API request.
- Account Settings from
You can access these properties directly in your integration logic. For example, use context.id to get the unified model id, check context.before for the pre-request steps.
Example
Header Mapping Configuration:
{
"Authorization": context.authToken
}Explanation:
context.authTokenaccesses the authentication token from the API call context.Authorizationheader is set with the token for Salesforce authentication.
Request Path Bindings
Available Bindings
headers- Description: The HTTP headers from the Unified API call.
body- Description: The request body associated with the Unified API call.
query- Description: Mapped query parameters.
rawQuery- Description: The query parameters from the user's request before
querymapping.
- Description: The query parameters from the user's request before
context- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
- Account Settings from
integratedAccount.context: These are persistent configurations specific to the connected account. - Information from
baseContext: This is used for passing certain info in Sync Jobs, such as the number of records for pagination (e.g., total_records_size).
- Account Settings from
You can access these properties directly in your integration logic. For example, to access the
authToken, usecontext.authToken.- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
before- Description: Contains the result of the
before stepscall.
- Description: Contains the result of the
id- Description: Can be used for cases when
idis present in Query Params, for example in/crm/accounts/:id
- Description: Can be used for cases when
Example
Request Path Mapping Configuration:
{
"userId": query.user_id
}Explanation:
query.user_idaccesses the mappeduser_idparameter.userIdis used to construct or modify the request path.
Error Bindings
Available Bindings
error- Description: The error object containing error details returned by the underlying API.
headers- Description: The HTTP headers from the Unified API call.
body- Description: The request body associated with the Unified API call.
query- Description: Mapped query parameters.
rawQuery- Description: The query parameters from the user's request before
querymapping.
- Description: The query parameters from the user's request before
context- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
- Account Settings from
integratedAccount.context: These are persistent configurations specific to the connected account. - Information from
baseContext: This is used for passing certain info in Sync Jobs, such as the number of records for pagination (e.g., total_records_size).
You can access these properties directly in your integration logic. For example, to access the
authToken, usecontext.authToken.before- Description: Contains the result of the
before stepscall.
- Description: Contains the result of the
id- Description: Can be used for cases when
idis present in Query Params, for example in/crm/accounts/:id
- Description: Can be used for cases when
Response Bindings
Used in: Response Mapping
Purpose: Transform the API response into a user-friendly format.
Available Bindings
response- Description: The raw API response returned by the API call.
query- Description: Mapped query parameters.
rawQuery- Description: The raw query parameters from the user's request.
context- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
- Account Settings from
integratedAccount.context: These are persistent configurations specific to the connected account. - Information from
baseContext: This is used for passing certain info in Sync Jobs, such as the number of records for pagination (e.g., total_records_size). - Dynamic Runtime Values:
id: The unified model id that uniquely identifies the record.before: The before steps that run immediately before the API request.
- Account Settings from
You can access these properties directly in your integration logic. For example, use
context.idto get the unified model id, checkcontext.beforefor the pre-request steps.- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
headers- Description: HTTP headers in the API response.
body- Description: The request body associated with the Unified API call.
Example
Response Mapping Configuration:
{
"id": Id,
"owner": { "id": OwnerId },
"name": Name
}Explanation:
Idmaps Salesforce'sIdto the API'sid.OwnerIdmaps to a nestedowner.id.Namemaps directly tonamein the response.
Final API Response:
{
"id": "0012w000024KwDeAAK",
"owner": {
"id": "0052w00000CkYXHAA3"
},
"name": "Truto-Archith-Test"
}Response Header Bindings
Used in: Response Header Mapping
Purpose: Manage HTTP headers in the API response.
Available Bindings
headers- Description: HTTP headers in the API response.
query- Description: Mapped query parameters related to the response headers.
rawQuery- Description: The raw query parameters from the user's request.
body- Description: The request body associated with the Unified API call.
context- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
- Account Settings from
integratedAccount.context: These are persistent configurations specific to the connected account. - Information from
baseContext: This is used for passing certain info in Sync Jobs, such as the number of records for pagination (e.g., total_records_size). - Dynamic Runtime Values:
id: The unified model id that uniquely identifies the record.before: The before steps that run immediately before the API request.
- Account Settings from
You can access these properties directly in your integration logic. For example, use
context.idto get the unified model id, checkcontext.beforefor the pre-request steps.- Description: A unified object that gathers all the information your API call needs. It merges:
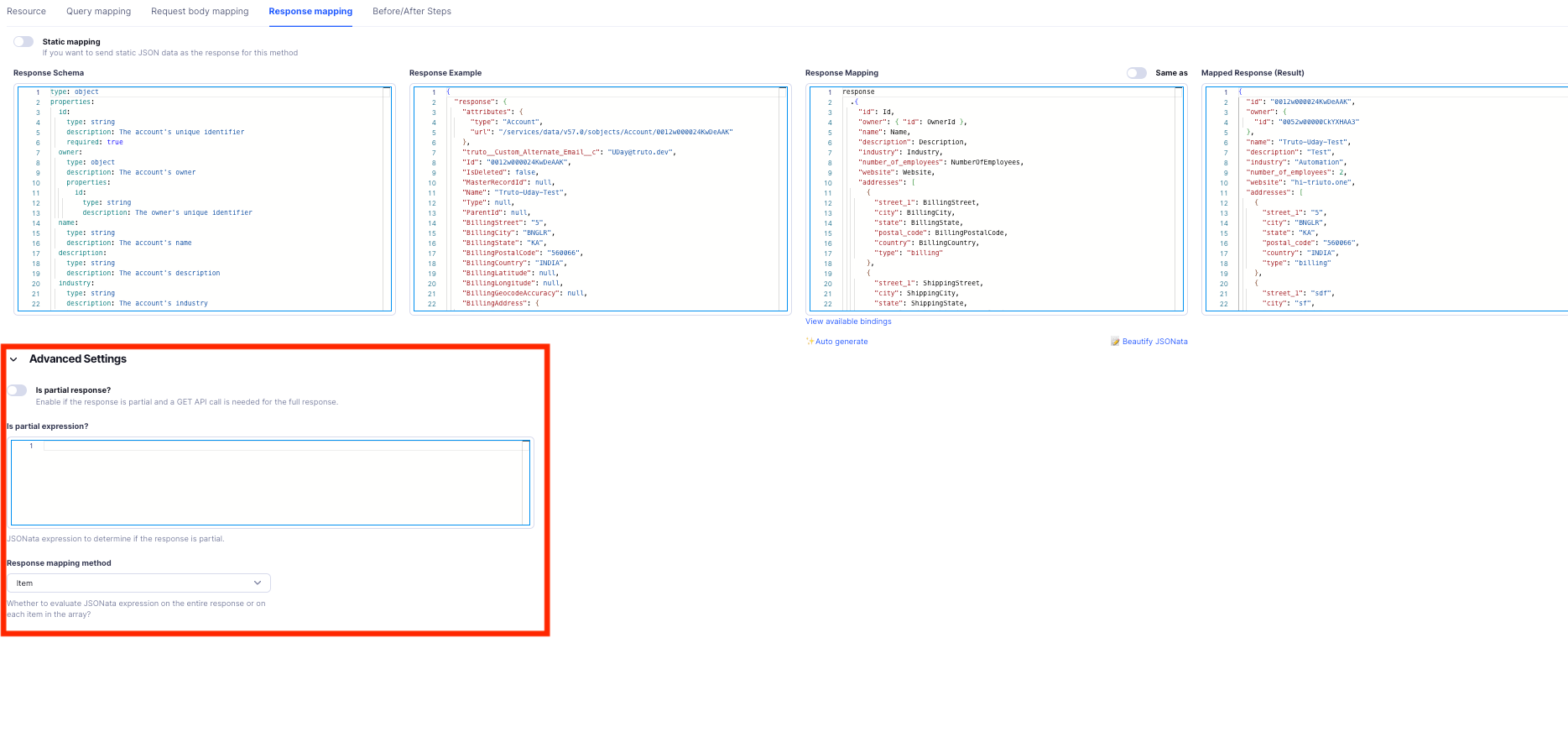
Is Partial Response?
Sometimes, the APIs you call may not return all the data you need in a single response. In such situations, you might need to make an additional API call to another endpoint to fetch the remaining data. To handle this, you can enable the Is partial response? option in the Advanced Settings of the Response Mapping configuration.
By default, this value is set to true when you enable this option. You can also define a JSONata expression that returns a boolean to validate whether the response is partial.
Available Bindings
query- Description: Mapped query parameters.
rawQuery- Description: The raw query parameters from the user's request.
before- Description: Contains the result of the
before stepscall.
- Description: Contains the result of the
id- Description: Can be used for cases when
idis present in Query Params, for example in/crm/accounts/:id
- Description: Can be used for cases when
rawBody- Description: Contains an
Array Bufferof thebody. Useful if the underlying API accepts data in a different formats likebase64.
- Description: Contains an
Before/After Steps
Available Bindings
id- Description: Can be used for cases when
idis present in Query Params, for example in/crm/accounts/:id
- Description: Can be used for cases when
query- Description: Mapped query parameters.
stepDescription: The step in before after/steps
The step object has the following attributes -
type- The type of the stepname- The name of the steprun_if- If thestepruns on certain conditions
context- Description: Contains all the variables stored in your Integrated Account.
body- Description: The request body associated with the Unified API call.
Practical Example
Scenario: Mapping Contact Resource
Map contact.id to the internal person_id used by Salesforce and then map it back in the response.
Step 1: Define Query Mapping
Query Mapping Configuration:
{
"person_id": query.contact.id
}Explanation:
query.contact.idaccesses thecontact.idparameter from the user's request.person_idis the internal parameter used by Salesforce.
Example Request:
GET /unified/crm/accounts?contact[id]=12345Mapped Query Parameters:
{
"person_id": "12345"
}Step 2: Define Response Mapping
Option 1: Using query Binding
Response Mapping Configuration:
{
"contact": {
"id": query.person_id
}
}Resulting API Response:
{
"contact": {
"id": "12345"
}
}Option 2: Using rawQuery Binding
Response Mapping Configuration:
{
"contact": {
"id": rawQuery.contact.id
}
}Resulting API Response:
{
"contact": {
"id": "12345"
}
}
